A Biomimetic SH2 Cross-coupling Mechanism for Quaternary sp3 – Carbon Formation
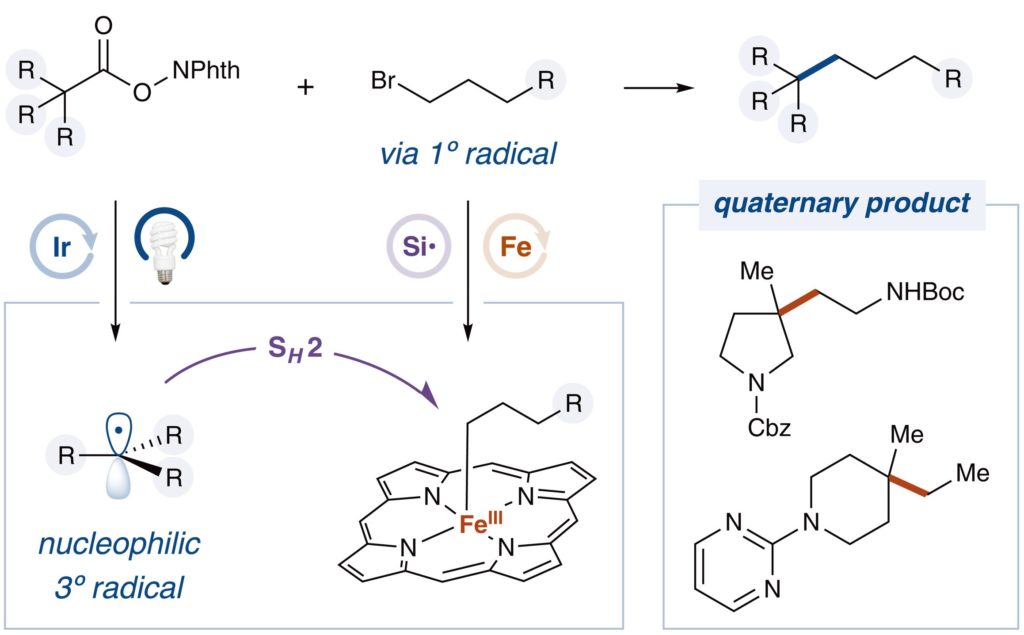
Recent work from the MacMillan group at Princeton University was published in Science Journal presenting a biomimetic SH2 cross-coupling mechanism for quaternary sp3-carbon formation. This study examined the cross-coupling between tertiary redox-active esters and primary alkyl bromides in the presence of Fe(OEP)Cl as an effective SH2 catalyst, in tandem with Iridium based photocatalyst and the […]
A Biomimetic SH2 Cross-coupling Mechanism for Quaternary sp3 – Carbon Formation Read More »