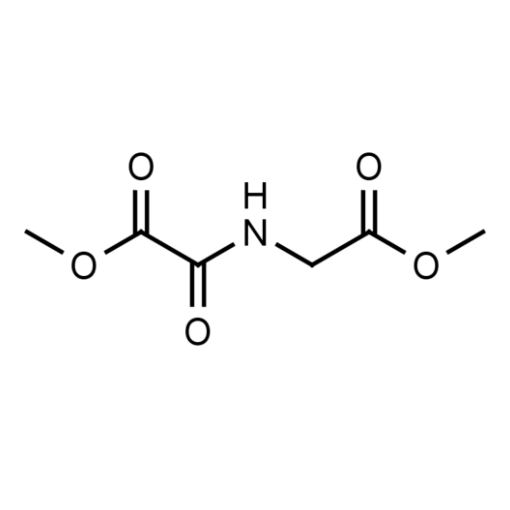
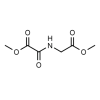
DMOG, also known as Dimethyloxalylglycine
Catalog#: D1070
D1070 Dimethyloxalylglycine TDS
D1070 Dimethyloxalylglycine SDS
CAS: 89464-63-1
MDL: MFCD05865098
Fields of Interest: Hypoxia inducer, Hypoxia Signaling, 2-OG-dependent dioxygenase inhibitor, HIF-alpha prolyl hydroxylase
Background: Dimethyloxalylglycine, also known as DMOG, is a glycine diester derivative that plays a role in neuroprotection inhibiting HIF-alpha prolyl hydroxylase.1,2 It is known as a hypoxia-mimetic and is widely used to study oxygen adaptive responses in cells. 3,4
Molecular weight: 175.14 g/mol
Molecular Formula: C6H9NO5
CAS Number: 89464-63-1
Storage: Store at –20 °C, under dry conditions.
Synonyms:
- dimethyloxalylglycine
- DMOG cpd
- N-(carboxycarbonyl)glycine
- N-oxalylglycine
- oxaloglycine
- oxalylglycine
References:
1.) King Hamish W, Michael Michael Z, Gleadle Jonathan M, Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells, BMC cancer (2012), 12421.
2.) Eckle, Tobias, Koehler, David, Lehmann, Rainer, El Kasmi, Karim C., Eltzschig, Holger K., Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 is Central to Cardioprotection, Circulation (2008), 118(2), 166-175.
3.) Chen, Haobin, Yan, Yan, Davidson, Todd L., Shinkai, Yoichi, Costa, Max, Hypoxic Stress Induces Dimethylated Histone H3 Lysine 9 through Histone Methyltransferase G9a in Mammalian Cells, Cancer Research (2006), 66(18), 9009-9016.
4.) Koditz Jens, Nesper Jutta, Wottawa Marieke, Stiehl Daniel P, Camenisch Gieri, Franke Corinna, Myllyharju Johanna, Wenger Roland H, Katschinski Dorthe M , Oxygen-dependent ATF-4 stability is mediated by the PHD3 oxygen sensor, Blood (2007), 110(10), 3610-7.