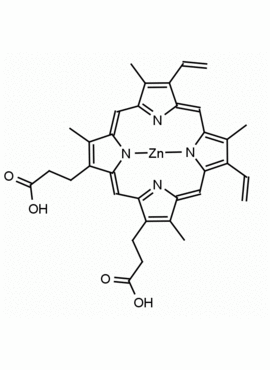
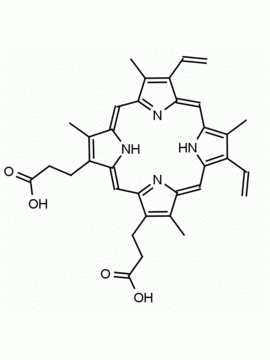
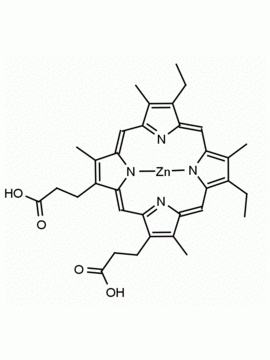
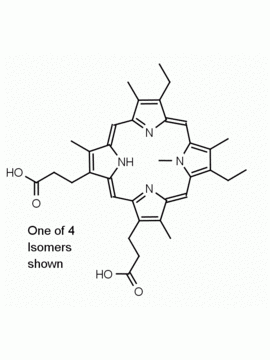
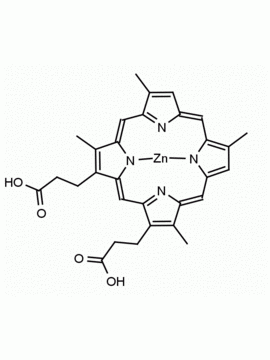
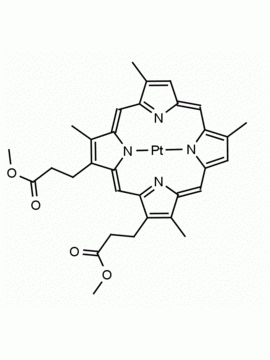
Zn(II) Protoporphyrin IX 8,13-Bis(vinyl)-3,7,12,17-tetramethyl-21H,23H-porphine-2,18-dipropionic acid zinc(II) CAS: 15442-64-5 MDL: MFCD00011612
Field of Interest: Natural Products Catabolism, Heme Oxygenase Inhibitor, Carbon Monoxide, Nitric Oxide, Gasosensors
Background: Zn(II) Protoporphyrin IX is a porphyrin based natural product that acts as a heme oxygenase inhibitor (HO-1) and is used to show retrograde messaging for long term potentiation in the hippocampus and the roles of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide in cell signaling. 1,2 It is also a high affinity ligand for soluble guanylate cyclases and affect the physiology of vasodilation and cardiovascular tissue. 3,4
Molecular weight: 626.03 g/mol
Molecular Formula: C34H32N4O4Zn
CAS Number: 15442-64-5
Storage: Store at room temperature, protect from light
Synonyms: Zinc protoporphyrin, PROTOPORPHYRIN IX CONTAINING Zn, Zinc protoporphyrin-9, Zn(PPIX), zinc-protoporphyrin IX
References:
1.) Hayashi, Shinobu; Takamiya, Rina; Yamaguchi, Tokio; Matsumoto, Kenji; Tojo, Shinichiro J.; Tamatani, Takuya; Kitajima, Masaki; Makino, Nobuya; Ishimura, Yuzuru; Suematsu, Makoto, Induction of heme oxygenase-1 suppresses venular leukocyte adhesion elicited by oxidative stress: role of bilirubin generated by the enzyme, Circulation Research (1999), 85(8), 663-671, DOI:10.1161/01.RES.85.8.663.
2.) Zhuo, Min; Small, Scott A.; Kandel, Eric R.; Hawkins, Robert D., Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide produce activity-dependent long-term synaptic enhancement in hippocampus, Science (Washington, DC, United States) (1993), 260(5116), 1946-50. DOI:10.1126/science.8100368.
3.) Stasch, Johannes-Peter; Schmidt, Peter M.; Nedvetsky, Pavel I.; Nedvetskaya, Tatiana Y.; Arun, Kumar H. S.; Meurer, Sabine; Deile, Martin; Taye, Ashraf; Knorr, Andreas; Lapp, Harald; et al, Targeting the heme-oxidized nitric oxide receptor for selective vasodilatation of diseased blood vessels, Journal of Clinical Investigation (2006), 116(9), 2552-2561. DOI:10.1172/JCI28371.
4.) Wang, Rui; Wang, Zunzhe; Wu, Lingyun, Carbon monoxide-induced vasorelaxation and the underlying mechanisms, British Journal of Pharmacology (1997), 121(5), 927-934. DOI:10.1038/sj.bjp.0701222.