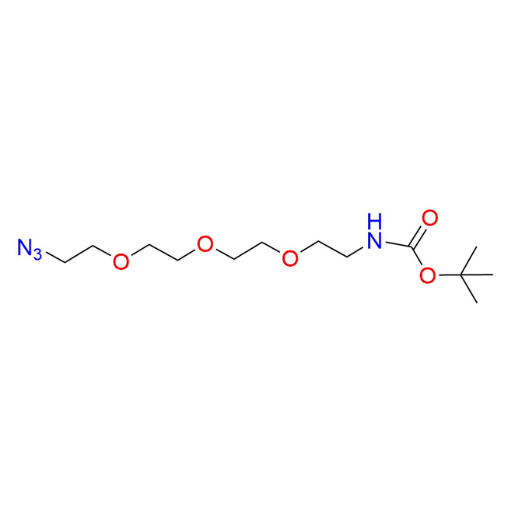
Name: tert-Butyl (2-(2-(2-(2-azidoethoxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate (97% purity)
Also available in deprotected forms suitable for direct bioconjugation and immediate amine coupling:
8-Azido-3,6-dioxaundecan-1-amine (99%)— AMTGC189-AD16-99
8-Azido-3,6-dioxaundecan-1-amine (98%)— AMTGC189-AD16-98
Molecular Formula: C13H26N4O5
CAS#: 642091-68-7
SMILES: O=C(OC(C)(C)C)NCCOCCOCCOCCN=[N+]=[N-]
MDL#: MFCD22056317
Catalog#: AMTGC187-AC16-97
Molecular weight: 318.37 g/mol
Other names:
- t-Boc-N-Amido-PEG3-Azide
- N3-PEG3-CH2CH2Nt-Boc
Fields of Interest: PEGylating reagent, Organic Synthesis, Medicinal Chemistry
Background & Applications:
Background
t-Boc-N-Amido-PEG3-Azide (CAS 642091-68-7) is a protected azide-functionalized PEG linker featuring a PEG4 spacer, a terminal azide group, and a Boc-protected amine. The polyethylene glycol backbone provides hydrophilicity, flexibility, and biocompatibility, while the azide functionality enables efficient bioorthogonal click chemistry, including CuAAC and strain-promoted cycloaddition. The Boc protecting group allows for controlled, stepwise synthesis by masking the amine during conjugation and can be readily removed under mild acidic conditions. This compound serves as a versatile intermediate within a robust portfolio of functionalized PEGs for precise molecular assembly.
Applications
This Boc-protected azido PEG linker is widely used in bioconjugation, drug delivery, and materials science applications requiring orthogonal reactivity and controlled functional group exposure. Common uses include the stepwise construction of PEGylated peptides and small molecules, preparation of multifunctional linkers, and surface or nanoparticle modification following deprotection of the amine. As part of a comprehensive functionalized PEG product line, t-Boc-N-Amido-PEG3-Azide supports modular design strategies for pharmaceutical research, diagnostics, and advanced biomaterials development.
Appearance: Pale yellow to amber liquid
Purity: 97%
Storage: 0-3 °C for long term storage
Solubility: EtOAc
Literature:
- Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2018, vol. 28, # 19, p. 3227 – 3230
- Chemical Communications, 2017, vol. 53, # 51, p. 6903 – 6905