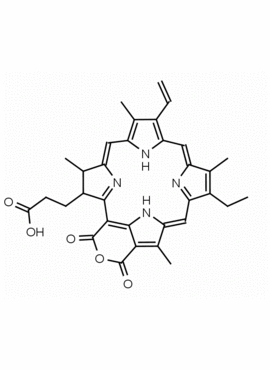
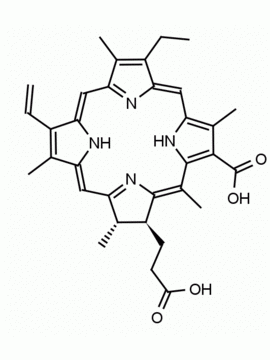
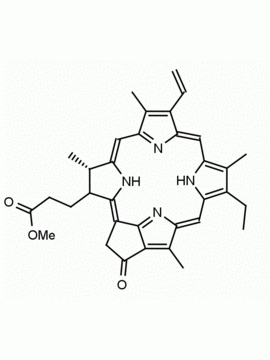
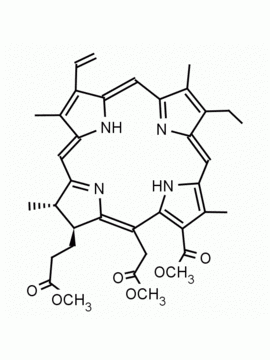
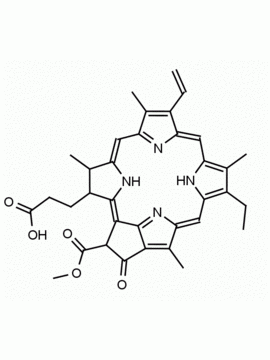
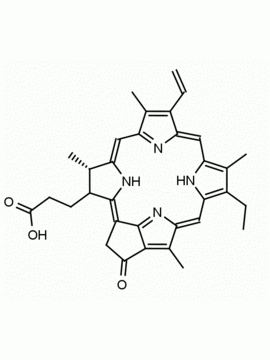
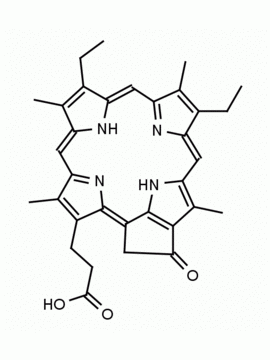
Purpurin 18 CAS: 25465-77-4 MDL: MFCD00672303
Molecular weight: 564.631 g/mol
Molecular Formula: C33H32N4O5
CAS Number: 25465-77-4
Storage: Store at room temperature, protect from light
Synonyms: Purpurin 18, 25465-77-4, 3-[(1E,10Z,15Z,19Z,
Field of Interest: Natural Porphyrins, Chlorophyll Derivatives, Photosensitizers
Background: Purpurin 18 is a natural porphyrin specialty chemical manufactured by Frontier Specialty Chemicals. Purpurin 18 has been used as a starting material for the synthesis of photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy applications.
References:
1.) Lee, et al. Use of the chlorophyll derivative, purpurin-18, for syntheses of sensitizers for use in photodynamic therapy. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1993, 2369-2377. https://doi.org/10.1039/P19930002369
2.) Cheng, et al. In Situ Monitoring Intracellular Structural Change of Nanovehicles through Photoacoustic Signals Based on Phenylboronate-Linked RGD-Dextran/Purpurin 18 Conjugates. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4, 1249–1258. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01922
3.) Pavlíčková, et al. PEGylated Purpurin 18 with Improved Solubility: Potent Compounds for Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Molecules 2019, 24(24), 4477; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244477
4.) Pavlíčková, et al. Advances in Purpurin 18 Research: On Cancer Therapy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(5), 2254; https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052254
5.) Zhang, et al. pH-Sensitive graphene oxide conjugate purpurin-18 methyl ester photosensitizer nanocomplex in photodynamic therapy. New J. Chem., 2018,42, 13272-13284. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ00439K
6.) Yeo, et al. Synthesis and Design of Purpurin-18-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Improved Anticancer Efficiency of Photodynamic Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14(5), 1064; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051064
7.) Liu, et al. Preparation of purpurin-18 loaded magnetic nanocarriers in cottonseed oil for photodynamic therapy. Materials Letters. Volume 62, Issues 17–18, 30 June 2008, Pages 2844-2847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.01.123
8.) Huang, P., Zhang, B., Yuan, Q. et al. Photodynamic treatment with purpurin 18 effectively inhibits triple negative breast cancer by inducing cell apoptosis. Lasers Med Sci 36, 339–347 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-020-03035-w
9.) Zheng, et al. Photosensitizers related to purpurin-18-N-alkylimides: a comparative in vivo tumoricidal ability of ester versus amide functionalities. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. Volume 10, Issue 2, 17 January 2000, Pages 123-127. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(99)00649-6
10.) Sharma, S., Dube, A., Bose, B. et al. Pharmacokinetics and phototoxicity of purpurin-18 in human colon carcinoma cells using liposomes as delivery vehicles. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 57, 500–506 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-005-0072-x