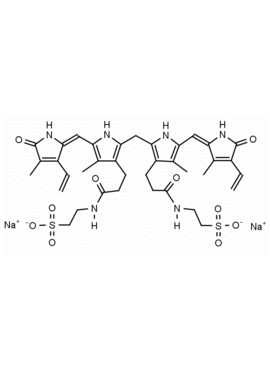
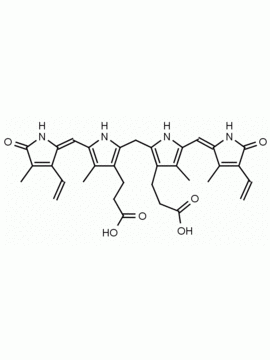
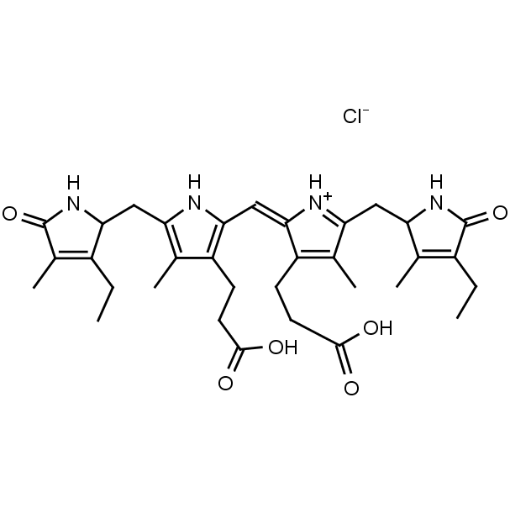
Bilirubin conjugate CAS: 68683-34-1 MDL: MFCD00044931
Molecular Formula: C37H244N6O10S2Na2
MW: 842.91
CAS: 68683-34-1
Storage: Store -20 °C under Argon or other inert gas. Hygroscopic in air, protect from light.
Purity: 95%
Alternative Names
Ditaurine amide of bilirubin (disodium salt); Disodium 2,2′-[(1,10,19,22,23,24-hexahydro-3,7,13,18-tetramethyl-1,19-dioxo-2,17-divinyl-21H-biline-8,12-diyl)bis[(1-oxopropane-3,1-diyl)imino]]bis[ethane-1-sulphonate]; Ethanesulfonic acid, 2,2′-[(2,17-diethenyl-1,10,11,19,22,23-hexahydro-3,7,13,18-tetramethyl-1,19-dioxo-21H-biline-8,12-diyl)bis[(1-oxo-3,1-propanediyl)imino]]bis-, sodium salt (1:2); 21H-Biline, ethanesulfonic acid deriv.; Ditaurobilirubin disodium salt
Field of Interest: Substrate for Proteins, Receptors and Transport Membranes and Indicator of Disease States
Background: Frontier Specialty Chemicals provides the bis-taurine conjugate of bilirubin as a surrogate for the natural digluconoride. Bilirubin conjugates are found prevalent in a variety of disease states related to jaundice and hepatocellular dysfunction.1,2 The conjugates are studied in cellular and animal models of disease, where binding to transport proteins and organic anion transporters has been established. 3,4 Its role in orphan disease states and hyperconjugation are the result of oxidation and inflammation processes in situ. 5
References:
(1) Konig et al., American Journal of Physiology, 278, G156 (2000)
(2) Stocker et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 84 5918 (1987)
(3) Cui et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 9626 (2001)
(4) Seppen et al., Journal of Clinical Investigation 94, 2385 (1994)
(5) Shoda et al., American Journal of Gastroenterology 96, 3368 (2001)