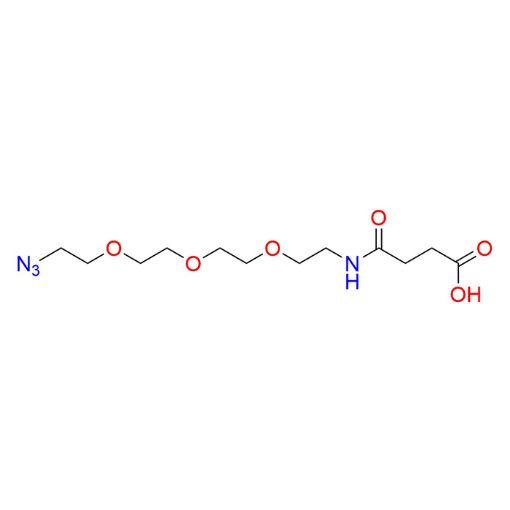
Name: 1-Azido-13-oxo-3,6,9-trioxa-12-azahexadecan-16-oic acid (99%)
Molecular Formula: C12H22N4O6
CAS#: 1202400-17-6
SMILES: O=C(CCC(O)=O)NCCOCCOCCOCCN=[N+]=[N-]
MDL#: MFCD20134138
Catalog#: AMTGC1238-AT24
Molecular weight: 318.33 g/mol
Other names:
- 16-AZIDO-5-AZA-4-OXO-8,11,14-TRIOXAHEXADECANOIC ACID
Fields of Interest: PEGylation, bioconjugation, click chemistry, drug delivery, materials science
Background & Applications:
Background
1-Azido-13-oxo-3,6,9-trioxa-12-azahexadecan-16-oic acid is a heterobifunctional azide-functionalized PEG linker featuring a PEG3 spacer that incorporates an internal amide linkage and terminates in a carboxylic acid. The polyethylene glycol backbone provides hydrophilicity, flexibility, and compatibility with aqueous and biological environments, while the amide functionality adds structural stability and polarity. The terminal azide group enables efficient bioorthogonal click chemistry, and the carboxylic acid can be readily activated for amide bond formation with amines or other nucleophiles. This multifunctional architecture makes the compound a valuable intermediate within a diverse portfolio of functionalized PEGs designed for controlled and site-specific conjugation.
Applications
1-Azido-13-oxo-3,6,9-trioxa-12-azahexadecan-16-oic acid is commonly used in bioconjugation, drug delivery, and materials science applications requiring orthogonal reactivity and defined PEG spacing. Typical uses include click-based attachment followed by carboxyl activation for coupling to peptides, proteins, or polymers, preparation of multifunctional linkers, and surface or nanoparticle modification. As part of a comprehensive functionalized PEG product line, this azido–amide–acid PEG supports modular design strategies in pharmaceutical research, diagnostics, biomaterials, and advanced materials development where stability and precise functional placement are critical.
Appearance: Pale green, viscous liquid
Purity: 99%
Storage: 0-3 °C for long term storage
Solubility: MeOH, Chloroform, EtOAc
Literature:
- Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2014, vol. 57, # 13, p. 5777 – 5791
- Chemical Communications, 2019, vol. 55, # 3, p. 369 – 372